VR-Exchange Capabilities
Protocol Translation & Bridging
MAK’s universal translator for distributed simulations. It performs FOM-to-FOM translation, RTI-to-RTI bridging, DIS or HLA-to-TENA translation, and can support simulation-to-C4I interoperability.
Learn all about VR-Exchange by clicking through the tabs below or download the VR-Exchange Capabilities document.
VR-Exchange Bridges Otherwise Incompatible Exercises
In general, bridging is necessary whenever it is not possible to achieve direct interoperability among a set of assets. Perhaps different federates have been developed to different FOMs, and were not developed using a FOM-Agile middleware toolkit like VR-Link. Bridging between the FOMs may be a more feasible solution than changing one set of federates to use the other federates' FOM. Perhaps one set of federates are using HLA 1.3 while others are using HLA 1516-2000, and you are not using an RTI that supports wire-compatibility between the two (such as the MAK RTI). Bridging may be a more feasible solution than upgrading the HLA 1.3 federates to IEEE 1516-2000. Perhaps different federate developers are used to running with specific RTI implementations, and are unwilling to switch to a common choice. Bridging may be a more politically palatable solution than arguing about whose RTI to use. Perhaps you have some HLA Federates and some TENA Federates that need to play in the same federation. Bridging may be the only way to achieve this goal.
The VR-Exchange Architecture - Brokers and Data Exchange
The VR-Exchange architecture consists of a protocol-independent Data Exchange called the Portal with a Broker for each supported protocol. Each Broker is then given a specific configuration to create a Connection. So, if you want to bridge two different RTI's, you would make two Connections which use the HLA 1.3 Broker, but configure each to point to a different RTI's LRC.
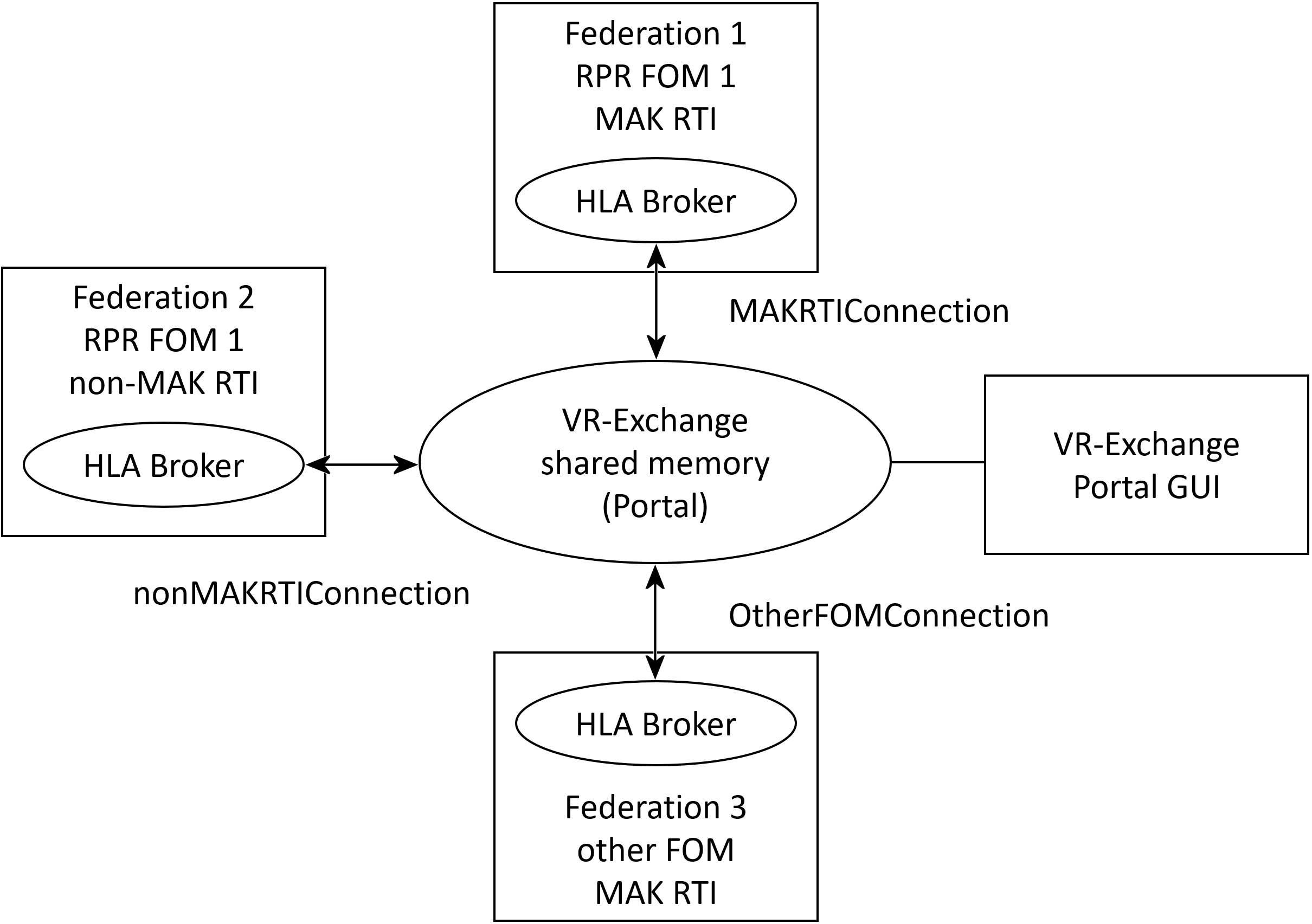
Each Connection runs as a separate process, and trades data with the other Connections through the Portal. The Portal creates and maintains a central shared memory pool through which Brokers connect. Although VR-Exchange is made up of several processes, all of the Connections are launched by the Portal, so you only need to launch a single executable.
The Portal provides a protocol-independent data representation for commonly used object and inter- action types - a lingua franca for interoperability among protocols. Each Broker is responsible for converting data between its local sub-federation's protocol or object model and the Portals's lingua franca.
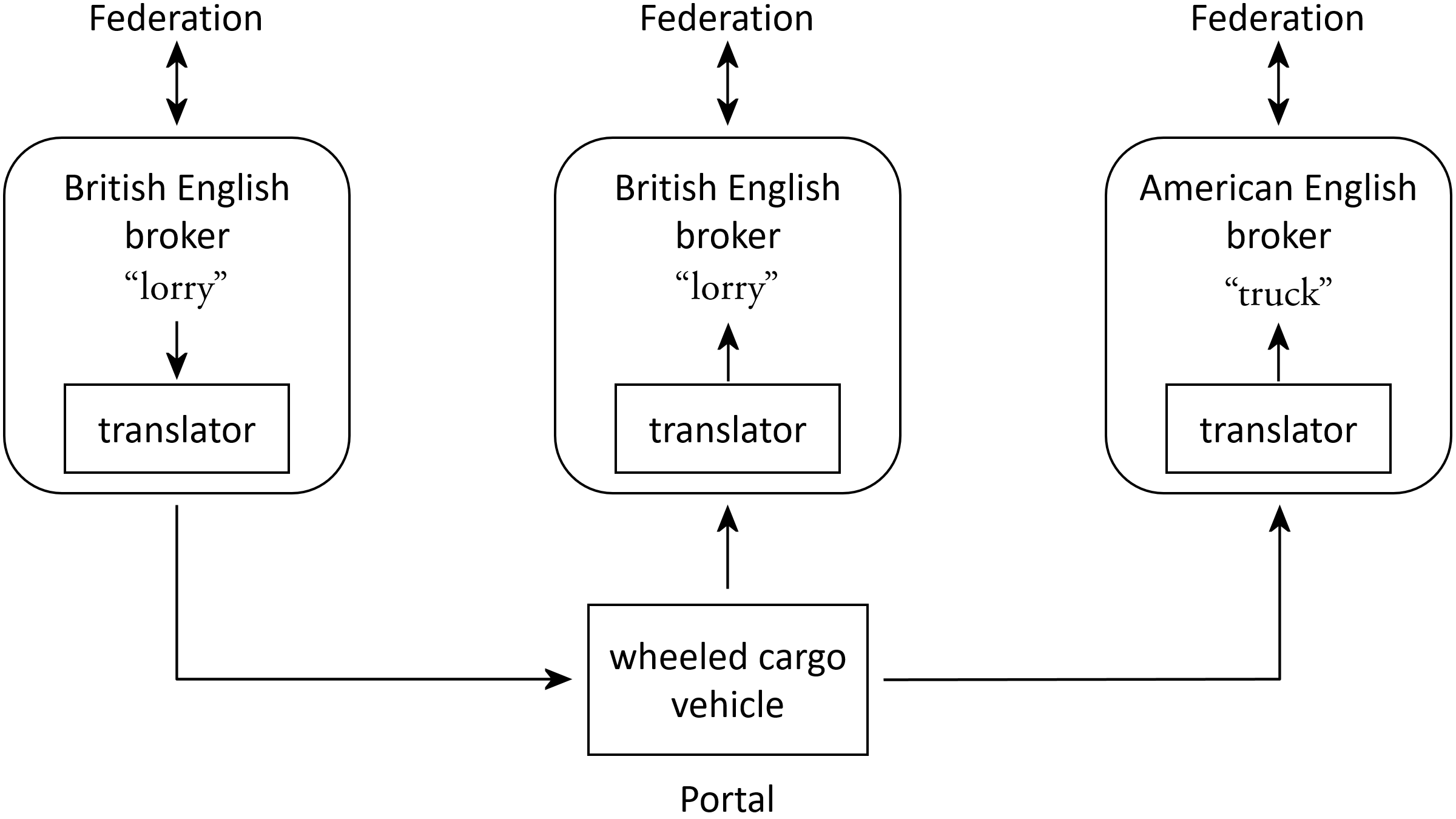
VR-Exchange Supports Many-to-Many Translation
VR-Exchange is not limited to only two connections at a time. It can be configured with several connections at once, allowing it to exchange data among three or more simulation environments. Each connection passes data that it receives from its own environment to the portal where it is made available to all of the other connections.
VR-Exchange Supports the "Federation of Federations" System Architecture
Historically, most distributed simulations have been more or less homogeneous. People have typically put together exercises where everyone used DIS, or where everyone used HLA through a particular RTI implementation and FOM. In those cases where both DIS and HLA federates needed to coexist, a DIS/HLA Gateway has been used. But federations that involved more than one RTI implementation, more than one FOM, or more protocols than just HLA and DIS have been rare.
In the last couple of years, things have changed: distributed simulations are more often being put together from existing assets, which have been built, tested, and verified against some set of pre-existing protocol choices. There is more integration between Live, Virtual, and Constructive assets. In addition, large exercises are becoming more common, with multiple sites connected over a Wide Area Network. These exercises are widely distributed not only in the sense of geography and network topology; the program management and organizational responsibility is also more likely than in the past to be distributed among many organizations. Each site manager might have his own budget, and might want to make his own decisions about what protocols to use.
The bottom line is that more and more people are thinking of these large distributed exercises as a "system of systems", or "Federations of Federations" problem. Each site wants to get their "sub-federation" built and tested independently, but they still want to be able to easily integrate with other sites on short time and money. Rather than spending time and money getting all of the sites, and all of the simulation assets to agree on a single architecture, it is often viewed as cheaper and easier to use an "Interoperability Portal" such as VR-Exchange to connect the sites. (This approach is often referred to as a "Mixed Architecture" design.
In many cases, the way this is done is by defining a "central" or backbone federation and requiring that each site use a portal like VR-Exchange to convert from their site's local federation, to the protocol, FOM, and RTI choice dictated by the central federation.
For example, the US Army's Electronic Proving Grounds' DTE5/MSDE experiment in September 2005 defined a central federation based on the MAK RTI and RPR FOM. Each site had the choice of connecting their federates directly to the central federation, or using a Gateway or interoperability portal to join. Several sites used the MATREX RTI and MATREX FOM, for example, but bridged into the central federation using VR-Exchange, which was configured to convert between the MATREX RTI / MATREX FOM and the MAK RTI / RPR FOM.
The US Air Force Distributed Mission Operations (DMO) program uses a similar "Federation of Federations" system architecture, as does the Canadian DND's War In a Box Program. (The latter uses MAK's VR-Exchange).
Pros and Cons of Using a "Federation of Federations"
From the technical side, getting everyone to agree on a common protocol, RTI, or object model is still usually the best approach. Your federates will be more tightly coupled, and you can take advantage of optimizations that in HLA, for example, only the RTI can provide (based on its knowledge of your overall network topology). For example, you lose some of the benefits of HLA DDM (Data Distribution Management) when going through a bridge. Ownership management and Time Management become more problematic. The MOM (Management Object Model) does not necessarily give you the answers you would expect, because no single RTI knows about all of the federates in the larger exercise. If your desire is really to achieve the "look and feel" of all federates participating in one, unified federation, then we recommend trying to use one, consistent RTI and FOM, if at all possible.
However, there are many situations where a distinct separation between different sets of federates is actually desirable! For example, in a "hierarchical federation", a group of federates might use an intra-simulator FOM to exchange data among components of a single vehicle simulator, but might want only "external" data such as position, velocity, and orientation to be available to other applications or sites. Perhaps different sub-federations are running at different levels of security, but still need to share some common data. Perhaps you would like to implement filtering at the site level, so that you have a single place from which to control what data can go between sites. Perhaps you want to be able to bring a running sub-federation in and out of a larger exercise. For these situations, a "Federation of Federations" system architecture is often the best solution.
Then there are the organizational benefits. As described above, the federation of federations approach often makes large-scale exercises easier to manage. Sub-federations on each site are free to choose their own interoperability architecture and object model, and can be independently developed, tested and verified. The integration effort to bring the sub-federations together becomes more manageable.
The bottom line is that if you feel that these improvements to the process of setting up an exercise outweigh the technical advantages of putting together a single large-scale federation on top of a common RTI and object model, then the Federation of Federations or "Mixed Architecture" approach (based on an interoperability portal like VR-Exchange) is the right choice.
VR-Exchange Brokers
VR-Exchange includes brokers for:
- HLA 1.3, IEEE 1516-2000, IEEE 1516-2010 (HLA Evolved). We provide FOM Mappers for RPR FOM 0.5, 0.7, 0.8, 1.0, 2.0 draft 14, 2.0 draft 17, and 2.0 draft 20. Also the ERF, MRF, MATREX, and AFMSTT FOMs. (Some of these might be restricted for our international customers.)
- HLA 1.3, IEEE 1516-2000, IEEE 1516-2010 (HLA Evolved) with time management.
- DIS.
- TENA (the Test and Training ENabling Architecture).
- DDS. The DDS Broker uses a custom object model that supports entity objects and the fire and detonate interactions.
- ADS-B (limited support).
- AviationSimNet (limited support).
- Cursor on Target (COT).
VR-Exchange can bridge between different versions of HLA (1.3 and 1516), or between different vendors' RTIs, and can translate between different FOMs. It can bridge between various TENA LROMs, or between TENA, HLA, and DIS.
VR-Exchange Supports JFCOM's LVC Bridge, or LVCDT Concept
VR-Exchange provides an architecture and implementation that are directly in line with JFCOM's Live, Virtual, and Constructive Data Translator concept. VR-Exchange has built-in support for HLA and TENA. Its architecture is flexible enough to support Brokers for Link-16 and various C4I protocols; and the ability to support simulation-to-C4I interoperability was one of VR-Exchange's key design criteria.
VR-Exchange Supports Many Objects and Interactions
VR-Exchange can handle any arbitrary object and interaction classes out of the box. If you are performing data translation, then each broker needs to convert data from the HLA FOM, TENA LROM, or other protocol on its side of the bridge to the protocol-independent data representation defined by the Data Exchange. The Data Exchange provides a built-in protocol-independent data representation for a wide variety of objects and interactions.
The following table lists the translation capabilities of each broker.
Translator | HLA | DIS | DDS | TENA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Acknowledge | X | X | X | |
Action Request | X | X | ||
Action Response | X | X | ||
Active Sonar | X | X | ||
Additional Passive Activities | X | X | ||
Aggregate | X | X | X | |
Areal Object | X | X | ||
Collision | X | X | X | |
Comment | X | X | X | |
Create Entity | X | X | ||
Data | X | X | X | |
Data Query | X | X | ||
Designator | X | X | X | |
Detonation | X | X | X | X |
Emitter System | X | X | X | |
Entity State | X | X | X | X |
Environment Process | X | X | X | |
Event Report | X | X | ||
Fire | X | X | X | X |
Gridded Data | X | X | ||
IFF | X | X | ||
Linear Object | X | X | ||
Logger Control | X | X | ||
Point Object | X | X | ||
Propulsion Noise | X | X | ||
Radio Receiver | X | X | X | |
Radio Signal | X | X | X | |
Radio Transmitter | X | X | X | |
Remove Entity | X | X | ||
Repair Complete | X | X | ||
Repair Response | X | X | ||
Resupply Cancel | X | X | ||
Resupply Offer | X | X | ||
Resupply Received | X | X | ||
Service Request | X | X | ||
Set Data | X | X | X | |
Start | X | X | X | |
Stop | X | X | X | |
Transfer Control | X | X |
If you have a requirement to pass additional kinds of data across VR-Exchange, the Data Exchange's lingua franca can be extended to cover the new object and interaction concepts. Extensions can be added either by MAK or by you (through the API).
DIS PDUs Supported
VR-Exchange supports the following PDUs (listed by protocol families):
- Entity Information and Entity Interaction PDUs
- Entity State PDU
- Collision PDU
- Warfare PDUs
- Fire PDU
- Detonation PDU
- Simulation Management PDUs
- Start/Resume PDU
- Stop/Freeze PDU
- Acknowledge PDU
- Action Request PDU
- Action Response PDU
- Data Query PDU
- Set Data PDU
- Data PDU
- Event Report PDU
- Comment PDU
- Create Entity PDU
- Remove Entity PDU
- Radio Communications PDUs
- Transmitter PDU
- Signal PDU
- Receiver PDU
- Distributed Emission Regeneration PDUs
- Electromagnetic Emission PDU
- Designator PDU
- IFF PDU
- Logistics PDUs
- Service Request PDU
- Resupply Offer PDU
- Resupply Received PDU
- Resupply Cancel PDU
- Repair Complete PDU
- Repair Response PDU
- Entity Management PDUs
- Transfer Control Request PDU
- Synthetic Environment PDUs
- Environmental Process PDU
- Gridded Data PDU
- Areal Object PDU
- Linear Object PDU
- Point Object PDU.
- Logger Control PDUs (for MAK Logger)
The VR-Exchange API Lets You Build Custom Brokers
VR-Exchange's open architecture means that you can develop custom brokers for your own protocols. We provide a documented interface (API) to the Data Exchange, as well as sample code that shows how to read and write to our protocol-independent data format. You don't have to write a separate translator between your protocol and every other protocol you need to interoperate with. Once you are able to translate your protocol to the lingua franca used by the Data Exchange, your data can be read by any of the other VR-Exchange brokers, and passed on to their federations.
VR-Exchange provides a base class called DtBroker, which can be subclassed to build new brokers for custom protocols. (The built-in DtHLABroker and DtTENABroker are derived from DtBroker as well.) The DtBroker base class automatically initiates and manages a DtPortalConnection - your connection to the central portal executable, and its shared-memory-based Data Exchange.
VR-Exchange's libPortal library contains a variety of classes that help you pass data in and out of the Data Exchange. DtPortalObjectPublishers allow you to publish objects through the Data Exchange, based on data that your broker has received from your protocol. DtPortalReflectedObjectManagers manage the objects that are coming through the Data Exchange from other Brokers. You can use DtPortalReflectedObject member functions to grab data about these remote objects, so that you can translate and send the information via your custom protocol. For those who have used MAK's VR- Link API, you will find these "publisher" and "reflected object" concepts very familiar. The libPortal library similarly provides DtPortalInteraction classes for sending and receiving interactions or events through the Data Exchange.
The API Lets You Extend VR-Exchange
If you need to extend the set of object or interaction classes that VR-Exchange can handle, the VR-Exchange API allows you to do this. You can extend VR-Exchange's lingua franca (the protocol-independent data representation defined by libPortal), to add new kinds of DtPortalObjectPublishers, DtPortalReflectedObjects, and DtPortalReflectedObjectManagers. In the newest version of VR- Exchange, you can also add new attributes to existing kinds of objects without needing to create one. The API uses C++ templates to ease the job of adding new types. You can define a new kind of DtPortalObject in one place, and use template instantiation to generate the publisher, reflected object, and reflected object list for the new type. Once you've extended the Data Exchange in this way, you can extend both the built-in and custom brokers, so that they can pass the new types through the Data Exchange.
VR-Exchange Supports High Performance
Performance will always be best if you can get all of your federates to agree on a single interoperability protocol, RTI implementation, and object model. Any time you put a bridge between a set of federates, there will always be some impact on performance. However, like all MAK Products, VR-Exchange was built with high-performance as a key requirement. In general, VR-Exchange adds only a small amount of latency, due to the additional network hop. Because of VR-Exchange's multi-threaded, shared-memory-based architecture, the amount of time a piece of data actually spends passing through VR-Exchange is typically negligible. VR-Exchange can easily keep up with exercises that contain thousands of objects (assuming the RTI or TENA Middleware you have chosen can keep up!)
VR-Exchange is Easy to use
VR-Exchange has a graphical user interface (Portal application) that provides a view into the shared memory space. The Portal application does not control the translation process. Translation takes place in the brokers. Users can configure all aspects of VR- Exchange through the GUI, as well as understand what's going on in each of their connected networks.
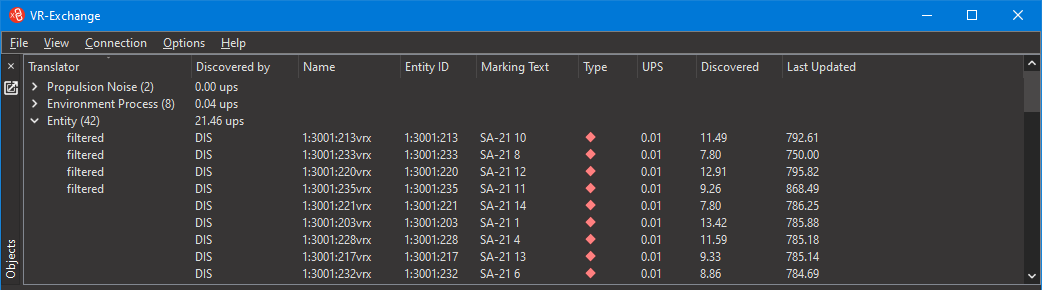
VR-Exchange displays lists of the objects and interactions that it discovers, which connection is publishing them, and statistics about them . As objects join and leave the exercise, VR-Exchange updates the display so that it only shows currently simulated objects.
Control Your View of Portal Data
When there are many objects listed in the Objects window, it can be difficult to find a particular object that you want to examine. You can search the objects list to quickly find particular objects. VR-Exchange searches the Name, Entity ID, and Marking Text columns in sequence to find the search string.
You can filter out entire classes of objects. You can also filter individual objects. You might do this if you are interested in particular objects and want to reduce network traffic by filtering out the objects you are not interested in. You can filter objects by name, entity type, and marking text. Filtering by entity type and marking text only applies to entities and aggregates.
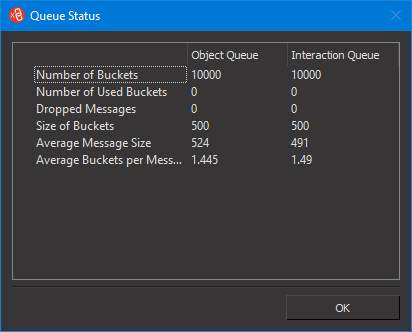
Display Details about the Shared Memory Queue
You can display details about the shared memory queue.
View Statistics
You can display a graph of the number of packets being processed by VR-Exchange and internal VR-Exchange messages.
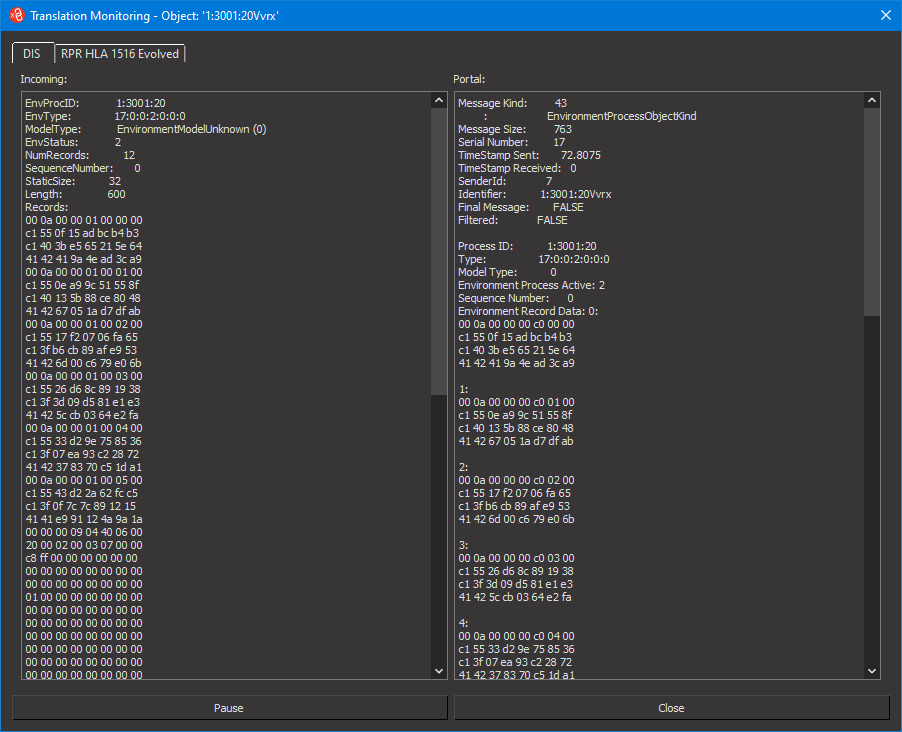
Monitor Translation on a Per-Object Basis
You can monitor translation on a per-object basis. When you monitor an object, VR-Exchange shows the most recent input and output for the object. This information can be useful for debugging brokers.
Superior Technical Support
At MAK, technical support is not just an afterthought. Our reputation for supporting our customers is one of the key reasons that people choose our products. When you call or e-mail us with questions, you speak directly to our product developers who know the software inside and out. When you buy MAK's products, you can be sure that MAK will be in your corner as you work towards successful completion of your project. We've even been known to be on the phone with customers during their HLA certification process, or during key events.
When someone reports a bug, our engineers are quick to provide a patch or workaround, meaning you will not have to wait for the next release to have your problem addressed.
If you need assistance that goes beyond the scope of technical support, our engineering services group is available to do VR-Exchange customization, extension or integration.
With maintenance, you are entitled to upgrades when they are released. Typically, new releases not only add support for the latest versions of RTIs, the RPR FOM, HLA Specifications, and so on, but also try to maintain compatibility with older versions as well. For example, our current release supports many versions of the MAK RTI, includes FOM Mappers for RPR FOMs 0.5, 0.7, 0.8, 1.0, and 2.0, and supports DIS 4, 5, 6, and 7.

